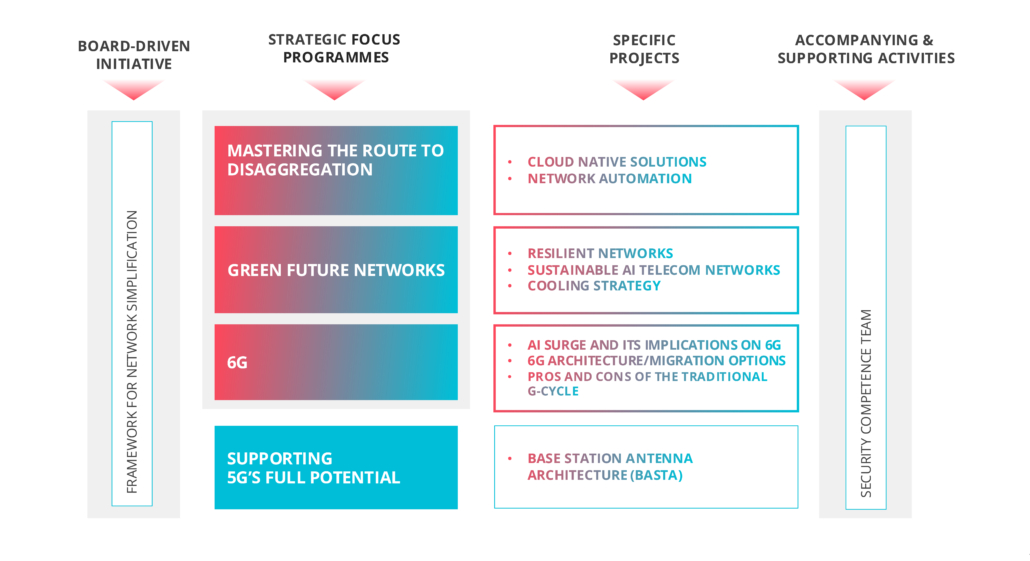
Strategic Focus Topics
NGMN’s Strategic Focus Topics reflect its objectives and working principles, focusing on the priorities set by the NGMN Alliance Board.
These topics are continuously adapted to align with NGMN’s evolving priorities, ensuring responsiveness to the mobile industry’s changing landscape.
For 2025 and beyond, NGMN’s priorities are 6G guidance and requirements including driving 5G’s full implementation and advancing the three Strategic Focus Topics:
- Mastering the Route to Disaggregation
- Green Future Networks
- 6G
Framework for Network Simplification
Project Lead:
- Assen Golaup, Liberty Global
MNOs manage complex legacy and new networks while facing rising data demand, evolving technologies, and commercial pressures. To stay efficient and sustainable, they must simplify architectures and operations, embrace AI, adapt practices, and follow a clear simplification framework.
The aim of this project is to outline the scope that MNOs would need to target in their transformation towards a simplified network. This project defines the key drivers for Network Simplification and define a high-level framework that operators can adopt when assessing the scope of the transformation required.
The project is structured into two phases:
- Phase 1: a simplified version to highlight challenges in achieving simplification. Phase 1 is planned to be finalised in Q4/2025
- Phase 2: focuses on MNOs and vendors experiences in addressing those challenges to achieve simplification benefits
NGMN’s operator-driven approach ensures that this framework is rooted in real-world challenges and aligned with industry needs. It complements existing NGMN work on 6G and Network Automation while offering a comprehensive perspective on how simplification can be achieved across all network domains.
For questions please reach out to the designated NGMN Senior Programme Manager Amr Saeed at amr.saeed@ngmn.org.
Mastering the Route to Disaggregation
LEADING IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF OPEN, DISAGGREGATED, VIRTUALISED AND CLOUD NATIVE SOLUTIONS
Cloud Native Solutions
Following the publication of the Cloud Native Manifesto, NGMN has setup a new project in collaboration with the CNTi (Cloud Native Telecom Initiative) of LF Networking, envisioning a Cloud Native Assessment Methodology that provides valuable insights to the industry. Prime objective is to provide guidance to organisations committed to embark transformation journeys adopting Cloud Native networks by identifying prerequisites, requirements, and level of maturity of cloud nativeness. The project has moved into its initiation phase, by charting their Project Description followed by the contribution phase.
Cloud Native Next Chapter – Operating Models with GenAI
Objectives:
This project outlines an overview on existing Assessment Methodologies of Cloud Native Network– focusing on telecom-specific adaptations in technology, processes, and skills. It defines a phased roadmap for integrating GenAI into telecom operating models and provides actionable guidance on AI-driven DevOps, predictive AIOps, customer-centric observability,
- Overview of existing Maturity Assessment Methodologies for cloud native networks.
- Determining assessment levels required to embrace GenAI, including evaluation of network maturity to determine readiness for GenAI adoption.
- Motivation for integrating GenAI in the context of cloud native networks, including identification of use cases, drivers, opportunities, and implications.
For questions please reach out to the designated NGMN Senior Programme Manager Sparsh Singhal at sparsh.singhal@ngmn.org.
Network Automation and Autonomy Based on AI
Objectives:
To achieve the transformation from network automation to autonomy through AI technology, NGMN will further conduct an analysis of technical requirements and implementation architecture research for network autonomy based on the network automation platform in this project.
From the perspective of technical and ecological requirements, in-depth discussions will focus on utilising open industrial cooperation models to consolidate industry consensus, unify technical approaches, provide R&D reference implementations, formulate industry standards, and promote the transition of the network from automation to autonomy.
The project produced a series of key publications, offering strategic guidance to the industry:
MLOps for Highly Autonomous Networks (February 2025)
Automation and Autonomous System Architecture Framework Phase 2 V1.0 (October 2024)
Automation and Autonomous System Architecture Framework V1.0 (November 2022)
For questions please reach out to the designated NGMN Senior Programme Manager Sparsh Singhal at sparsh.singhal@ngmn.org.
Green Future Networks
BUILDING SUSTAINABLE & ENVIRONMENTALLY CONSCIOUS SOLUTIONS
Project Lead:
- Marie-Laure Lamouroux, Orange
With Green Future Networks, NGMN is enabling the mobile industry to further transform and meet its environmental and sustainability goals. Since the initiative started in 2021, we have identified the key opportunities and challenges and made actionable recommendations on several key areas.
Recently, Phase 4 of the Green Future Networks Programme has been concluded and Phase 5 has been inititated.
Phase 5 Projects:
- Resilient Networks
- Sustainable AI Telecom Networks
- Cooling Strategy
Resilient Networks
The project focuses on the definition of resilience in the context of telecommunication networks, the introduction of risks and related scenarios and the principles of resistance to these risks.
Sustainable AI Telecom Networks
Defining metrics and measurement methods to characterize AI energy consumption and energy efficiency holistically, from a whole life cycle analysis (LCA) perspective, to enable sustainable AI-native telecom networks.
Cooling Strategy
Identify the common challenges facing Mobile Operators in terms of energy demands and cooling needs, considering data growth; analyse a set of suitable cooling solutions; outline cooling strategies to address a variety of environmental and climate conditions.
The Green Future Networks Programme published the following deliverables during phase 1 – phase 4:
Metering in RAN Transport Networks (December 2025)
Energy Management and Flexibility in Mobile Networks (July 2025)
Environmental Sustainability and Reporting (May 2025)
A Roadmap to Energy Efficient Mobile Networks (July 2024)
Metering in Virtualised RAN Infrastructure (April 2024)
Reducing Environmental Impact (January 2024)
Network Energy Efficiency Phase 3A (December 2023)
Network Energy Efficiency Phase 2 (October 2023)
For questions please reach out to the designated NGMN Senior Programme Manager Amr Saeed at amr.saeed@ngmn.org.
6G
GUIDANCE AND REQUIREMENTS RELATED TO DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS AND NETWORK ARCHITECTURE EVOLUTION
Project Co-Leads:
- Quan Zhao, China Mobile
- David Lister, Vodafone
Objectives:
Our main focus in 2025/26 is providing guidance and key requirements for design considerations and network architecture evolution:
- Deliver impactful 6G insights and guidance from an operator’s perspective in order to provide timely guidance to the industry
- Play a key role in avoiding fragmentation of global 6G standards and ecosystem to achieve affordable deployments
- Identify a set of high-level business drivers including social responsibility aspects and MNO operational aspects
- Develop requirements by taking a customer centric view
- Engage with different stakeholders, monitor external 6G activities and facilitate bilateral exchange with external organizations at the right time
- Identify and analyse relevant SDO’s and industry organisations to maximize NGMN’s impact
This collaborative approach aims to streamline networks, improve efficiency and deliver clear customer value.
Phase 6 of the 6G Programme is being initiated with multiple deliverables:
AI Surge and its Implication on 6G
- Architecture Study: Agentic core vs. traditional 5G-SA: assessing the architectural change for AI ready network
- Network for AI and AI for Network: association between AI and end-to-end network infrastructure
- Impact of AI traffic on Network – AI traffic models considering end to end traffic including overall traffic
6G Architecture/Migration Options
The following deliverables have been published in the 6G Programme in the previous phases:
- 6G Key Messages – An Operator View (June 2025)
- Network Architecture Evolution towards 6G (February 2025)
- ITU-R Framework for IMT-2030 (February 2024)
- 6G Trustworthiness Considerations (October 2023)
- 6G Position Statement (September 2023)
- 6G Requirements and Design Considerations (February 2023)
- 6G Use Cases and Analysis (February 2022)
- 6G Drivers and Vision (April 2021)
For questions please reach out to the designated NGMN Senior Programme Manager Sparsh Singhal at sparsh.singhal@ngmn.org.
Framework for Future Communication Networks
The “Framework for Future Communication Networks” is a strategic NGMN Board-led project focused at supporting Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) in shaping the evolution of future networks. As new technologies emerge, user demands continue to grow and network operation requires simplification, it is essential for operators to take an active role in guiding how future communication systems are defined – including the position and potential of 6G.
This project provides targeted, operator-driven guidance on key principles and requirements that will influence the design and direction of future networks. It builds on NGMN’s earlier contributions, such as the “6G Position Statement” and the “Radio Performance Assessment Framework”, and introduces fresh perspectives on traffic forecasts, integrated network solutions and user experience enhancements.
With its unique position as an operator-led alliance, NGMN facilitates collaboration and alignment across its global membership, ensuring that industry evolution reflects the real-world needs.
The following deliverable has been published:
Further deliverables are expected in Q4/2025.
Security Competence Team
The project is a vertical activity that supports the NGMN Work Programme in aspects of security matters.
Project Lead:
- Xiaoting Huang, China Mobile
Objective:
SCT’s objective is to analyse security challenges and propose comprehensive security requirements and recommendations related to network architecture, deployment, and operational aspects for 5G and beyond. Additionally, the initiative supports security analysis and addresses related topics raised by other NGMN projects and teams, ensuring a robust and secure framework for future telecommunications.
Following deliverables were published:
Supporting 5G’s Full Potential
All projects not aligned with our three strategic focus topics fall under ‘Supporting 5G’s Full Potential’. Currently, this applies to the BASTA project, which is described below.
BASTA (Base Station Antenna Architecture)
Objective:
Provide the industry with an updated set of parameter definitions, measurement methodologies and reporting processes. This enables a uniform way to describe the electrical and mechanical characteristics of the network side of the radio link (Base Station Antenna).
Recommendation for Base Station Antennas V13.0 is a detailed technical reference document covering Active, Passive and Hybrid Antenna Systems. Providing RF, Electrical, Mechanical and Environmental Parameters and Recommendations. Beside Supporting XML files to allow digital data exchange between vendors and operators:
Utilizing this common approach for describing “base station antennas” enables more efficient and cost-effective planning, engineering, and operation of mobile networks. This approach helps ensure the high-quality mobile service that users, businesses, and industries require.
Previous to the above described unified BASTA project, the BASTA project consisted of two work streams: Active and Passive Antennas, that have published the following deliverables:
Active Antennas
- Recommendation on Base Station Active Antenna System Standards V1.0 (April 2020)
- Recommendation on Base Station Active Antenna System Standards V2.0 (August 2021)
- Recommendation on Base Station Active Antenna System Standards (September 2021)
- Recommendation on Base Station Active Antenna System Standards V3.0 (September 2023)
Passive Antennas
- Recommendation on Standards for Passive Base Station Antenna Systems V12.0 (April 2022)
- Recommendation on Base Station Antenna Standards V11.1 (March 2019)
For questions please reach out to the designated NGMN Senior Programme Manager Amr Saeed at amr.saeed@ngmn.org.